What You Need to Know About the Different Ways of Injection Methods Explained
Intravenous (IV) : This way gives medicine as a liquid directly into a vein. It’s fast and works right away. They use it for many things like giving fluids, pain relief, anesthesia, blood products, nutrition, contrast dye, steroids, chemotherapy, and monoclonal antibodies.
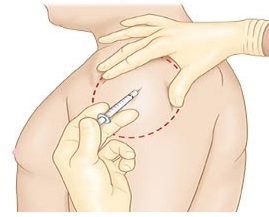
Intramuscular (IM) : This way puts medicine into a muscle. Muscles have lots of blood, so the body quickly takes in the medicine. They use it for vaccines, some antibiotics, corticosteroids, hormones, and certain psychiatric medications.
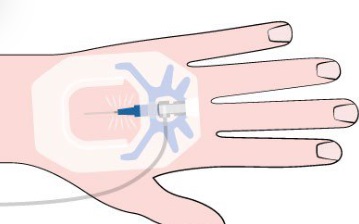
Subcutaneous (SC) : This way puts medicine under the skin in the fatty layer. It’s slower, and the body absorbs it over time. They use it for insulin, heparin, epinephrine, growth hormone, and some vaccines.
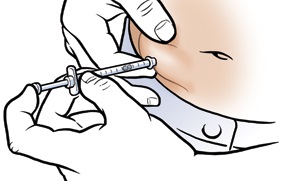
Intraosseous (IO): This way gets medicine into the bone marrow, which is full of blood vessels and spreads the medicine fast. They use it in emergencies when IV access is hard, like in cardiac arrest, shock, trauma, and severe dehydration.
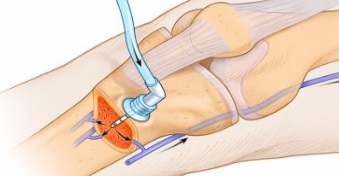
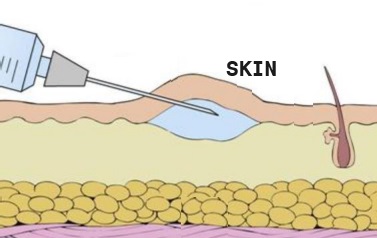
Intradermal (ID) : This way puts a small amount of medicine into the layer of skin below the outer layer. They use it for tests, like checking for allergies, tuberculosis, and leprosy.